Chapter 27: workshop on financial guarantees for covering the costs of waste management operations

In support of further harmonisation of national legislation with the Union acquis and its effective implementation in areas covered by Negotiation Chapter 27, the Policy and Legal Advice Center (PLAC III) project has organised a workshop on obtaining financial guarantees needed for waste management operations and transboundary movements of hazardous waste.
The workshop was organised with the assistance of the Ministry of Environmental Protection, which is also a beneficiary institution, on 25 February 2021. The PLAC III project has provided support in providing legal gap analysis of relevant domestic legislation, comparative analysis of best European practices and drafting of proposals for further harmonisation of regulations with relevant EU directives.
The basic principle in environmental protection in the European Union is “polluter pays” principle. Predictable financing based on this principle is needed to raise the level of investment in the sector. According to the European Commission reports, further progress is needed in Serbia in transposing and implementing the Environmental Liability Directive (ELD) 2004/35, the Waste Framework Directive 2018/851 and the Regulation on shipments of waste 1013/2006/EC in the field of financial guarantees, insurance and other financial instruments needed for covering the costs of waste management and transboundary movement of waste.
At the workshop, project expert Marko Ostoich presented a comparative analysis of examples of European practice. He said that the basic idea is to prevent damage to the environment through the given financial guarantees, whereby ELD especially refers to three types of damage: damage caused to protected species and natural habitats, to water and the soil contamination. The application of ELD differs significantly in EU Member States, and this also applies to the area of financial guarantees in waste management where it is a legal obligation in only eight countries. Ostoich presented two instruments – financial guarantees (which protect the institution) and environmental insurance (which benefit a private company or operator). In Italy, out of 20 regions, only in the Veneto region both financial instruments are mandatory by the law in the field of waste management.
Project expert Gordana Petković presented the results of the legal gap analysis of national legislation with Union acquis. The Law on Waste Management is to a high degree harmonised with the EU legislation, except in the part related to the closure of the facility, for which it is necessary to introduce an amendment that a financial guarantee is obligatory for the issuance of a permit. Petkovic also said that Serbia has yet to introduce collective schemes of producers. Recommendations for full transposition of relevant directives are to adopt amendments to the Law on Waste Management, the Draft Regulation on the financial guarantees or equivalent insurance for waste management operations and amendments to the Rulebook on the form of application for a permit for storage, treatment, recovery and disposal of waste and the Rulebook on the content and form of permit for waste management. PLAC III project drafted amendments to the Law on Waste Management, as well as amendments to regulations on financial guarantees in the field of waste management operations and to ensure transboundary movements of waste.
The workshop was attended by the representatives of the Ministry of Environmental Protection, the Provincial Secretariat for Urbanism and Environmental Protection, the City Administration of Belgrade, the City Administration of Novi Sad, operators and representatives of insurance companies.
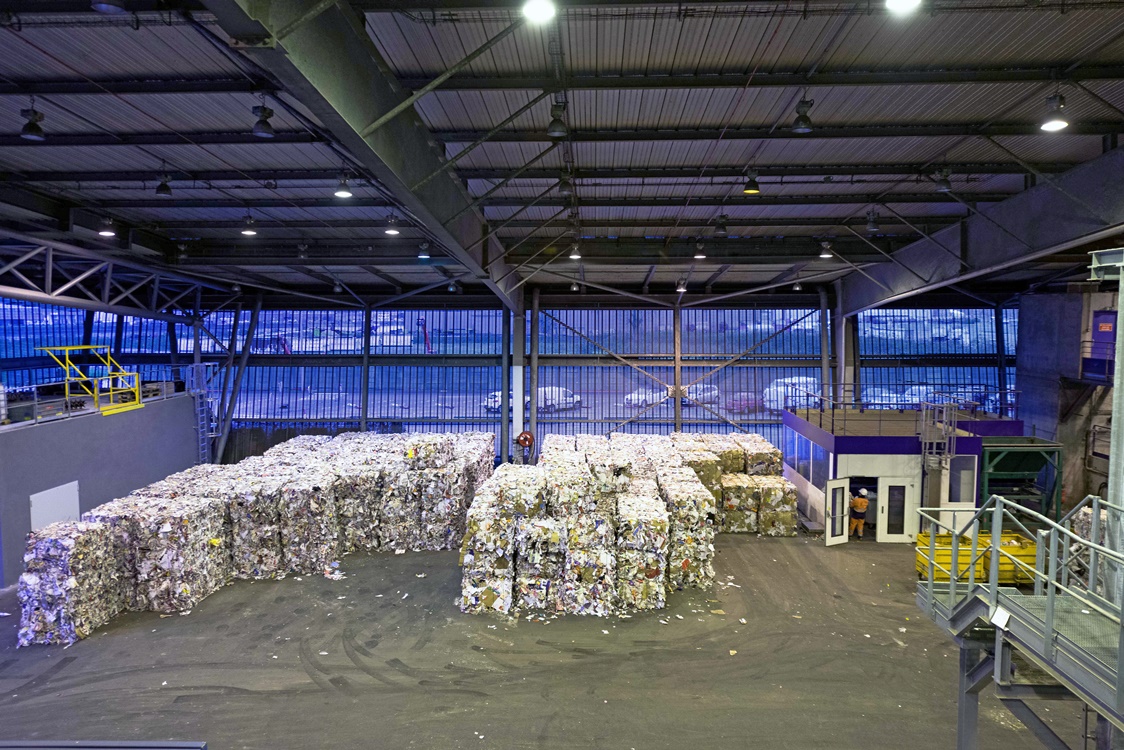
Cover photo: Audiovisual service, European Commission
Relevant EU legislation:
Photo gallery
Recent Posts

Notice
9. April 2024.

The fourth project brochure published
29. March 2024.

The last meeting of the Steering Committee
28. March 2024.
Negotiation chapters
- Chapter 1: Free movement of goods
- Chapter 3: Right of establishment and freedom to provide services
- Chapter 8: Competition policy
- Chapter 9: Financial services
- Chapter 10: Information society and media
- Chapter 11: Agriculture and rural development
- Chapter 12: Food safety, veterinary and phytosanitary policy
- Chapter 13: Fisheries
- Chapter 15: Energy
- Chapter 16: Taxation
- Chapter 27: Environment
- Chapter 28: Consumer and health protection
- Chapter 32: Financial control
- Chapter 33: Financial and budgetary provisions